Steemian Friends,
Today, I will discuss a transistor for electronics work. Although a transistor is a small electronic device, its function and importance are very high. Below, I will show the structure of a transistor and its measurement with a multimeter.
.jpg)
Thumbnail Photo
Transistors act as switching devices in electronic circuits. There are two types of transistors. Transistors are made of P-type and N-type semiconductors.
- PNP transistor
- NPN transistor

NPN Transistor Structure
I have shown the structure of a transistor in the picture below. PNP transistor is made of two P-type and one N-type semiconductor. On the other hand, the NPN transistor is composed of two N-type and one P-type semiconductor, as shown in the picture.
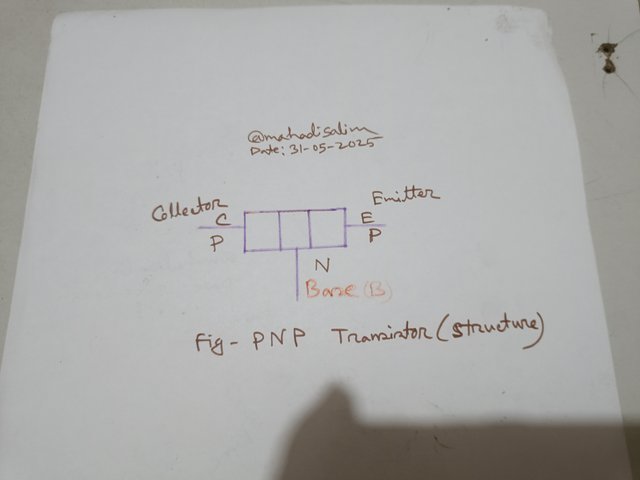
PNP Transistor Structure
A transistor has three terminals.
- Base
- Collector
- Emitter
Now, I will show you how to determine the base, collector, and emitter of a transistor using a multimeter. The terminals of a transistor are not marked. To be skilled in electronics, one must know how to identify the terminals of a transistor.
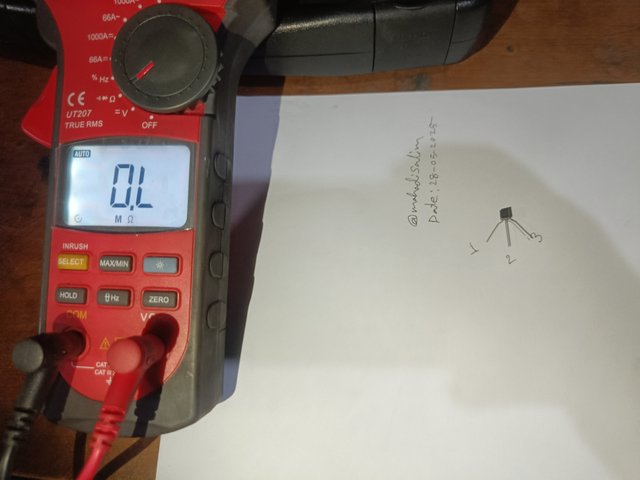
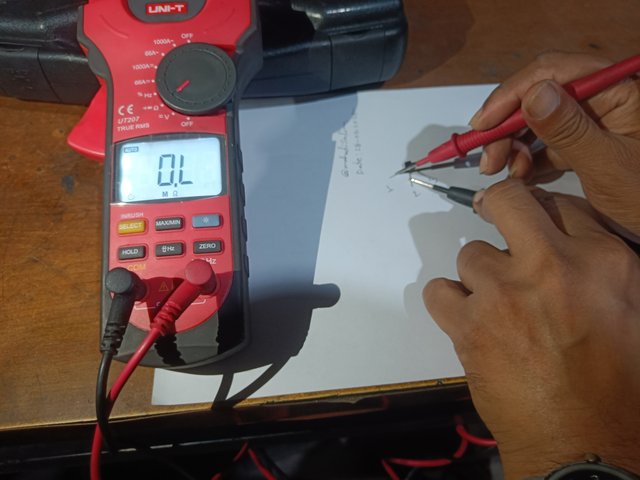
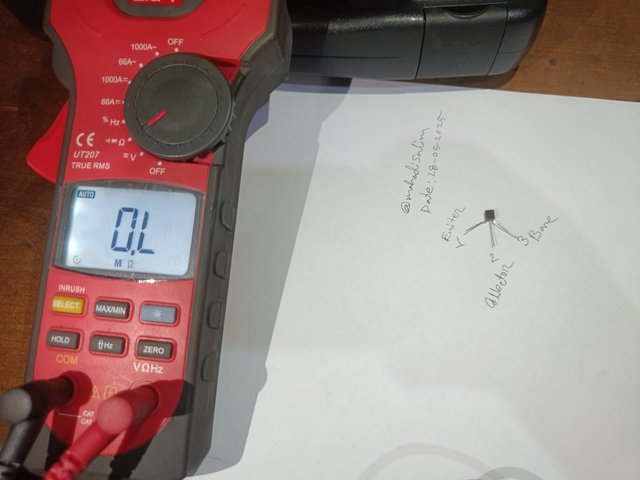
I create a small gap between the three terminals of a transistor, as shown in the figure below. Then, I mark the three terminals on paper as 1, 2 and 3. Then, I set the multimeter's selector switch to the ohms range. I have shown it in the picture.
 |  |
|---|
A transistor and multimeter setup in the ohms range
Then, I hold the black knob of the multimeter to the number one terminal of the transistor. Then I hold the red knob of the multimeter to the number two and three terminals. I do not see ohms on the multimeter. I have shown it in the picture below.
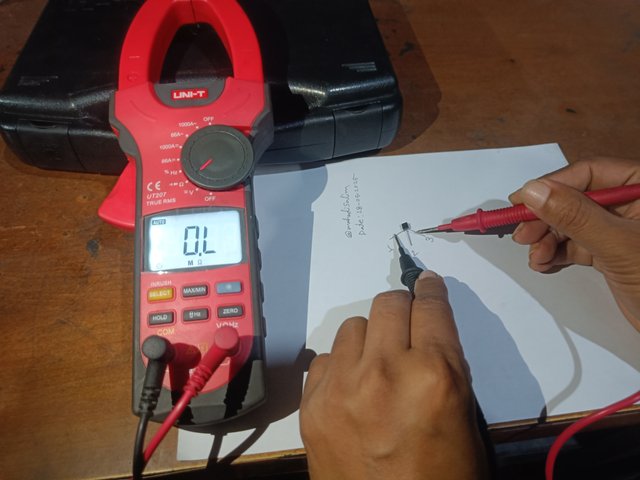 |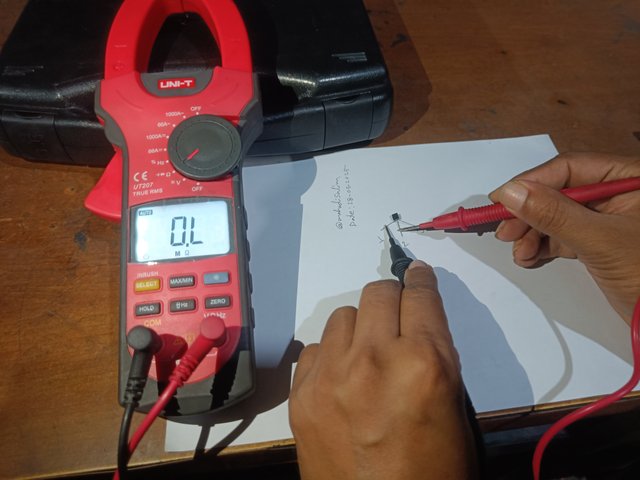  |
|---|
Check with a multimeter by holding the first terminal of the transistor to the common terminal.
Then, I hold the black knob of the multimeter to the number two terminal of the transistor. I have the red knob of the multimeter to the number one and three terminals. This time, I still do not see ohms on the multimeter. It is shown in the picture below.
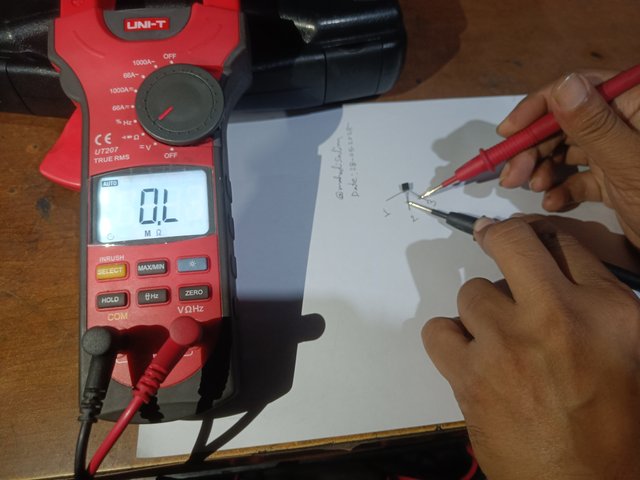 |  |
|---|
Check with a multimeter by holding the second terminal of the transistor at the common point.
Then, I hold the black knob of the multimeter to the number three terminal of the transistor. Now I have the red knob of the multimeter to the number one and two terminals of the transistor. Now I see two ohms on the multimeter. I measure 10.64 ohms on the first terminal of the transistor and 9.30 ohms on the second terminal.
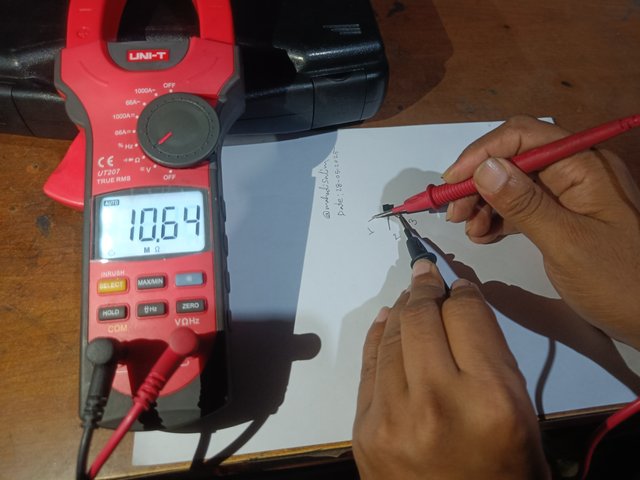 |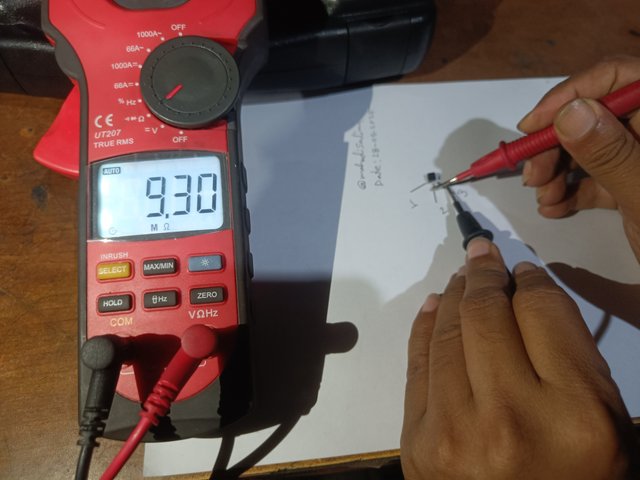  |
|---|
Check with a multimeter by holding the third terminal of the transistor common.
Result:
- I tested in the fourth step and found an ohm reading at terminals 1 and 2. Since the third terminal is the common terminal, it is the base of the transistor.
 |  |
|---|
Finally, the base, collector and emitter are identified.
The number one end has more ohms, so it is the Emitter. The end with higher ohms is the Emitter.
The resistance was low at terminal number two of the transistor, indicating it is the collector.
In the above process, the base, collector and Emitter of a transistor are checked with a multimeter. I have included the video below, which demonstrates how to find the base, collector, and Emitter of a transistor using a multimeter.
My YouTube Link



This is my Twitter share link :
https://twitter.com/mahadih83660186/status/1928687270518808682?t=dh7OTxoN9095va9aj199ZA&s=19
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit